What is an Operating Budget?
Discover how to create an operating budget and download a free template in Excel format. Includes frequently asked questions.
Updated on February 15th, 2022
The SMB Guide is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
An operating budget is typically prepared on an annual basis. It contains estimates of monthly expenses and revenue projections. An operating budget serves as a planning tool and helps businesses keep track of their profitability throughout the budgeted period.
Why an Operating Budget is Important:
An operating budget is an important tool for businesses to establish financial accountability and plan and manage resources. It helps businesses to track income and expenses, identify cost drivers, and assess how these can be reduced to optimize cost-efficiency and maximize overall profitability.
How to Create an Operating Budget:
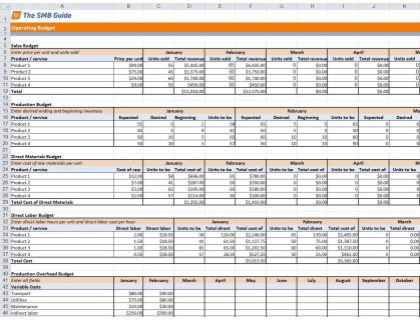
An operating budget encompasses several smaller or sub-budgets. The different budget components are pulled together into one comprehensive overview of the business's monthly revenue, costs, and expenses.
Operating Budget Template - Free Download
Use our operating budget template in Excel format to create an operating budget for your business.
1. Sales Budget.
The first step in creating an operating budget is to draw up a sales budget. This also doubles as a sales plan for the year. Begin by listing all the products and services you plan to sell along with their pricing. Then make monthly sales projections for the budget period, typically one year.
Use your past sales data and reports as a starting point. Also, keep in mind that seasonal changes, new product launches, and planned marketing activities may impact your potential sales.
Best Accounting Software
Information on the best accounting software companies, including Freshbooks, QuickBooks, and Sage. See pricing, features, comparisons, and more.
Dec 21, 2023
2. Production Budget.
A production budget helps you to plan exactly how many units of each product must be produced to meet your projected sales volume while maintaining sufficient inventory levels.
You will have to determine how much inventory you have to begin with and how many units of each product should make up your closing inventory at the end of each month. You can calculate the number of units that must be produced as follows:
Number of Units to be Produced = (Number of Expected Sales + Desired Closing Inventory) - Beginning Inventory
Use the number of expected sales from your sales budget.
Inventory Management Software
Compare the top inventory management software, with pricing, detailed feature information, customer reviews, and FAQs.
Dec 21, 2023
3. Direct Materials Budget.
Next, determine the number of direct materials that are needed to fulfill the requirements of the production budget. Direct materials are the raw materials needed to manufacture a product.
The total cost of raw materials required to produce each product item listed in the production budget is multiplied by the total number of products that must be produced each month to determine the total cost of direct materials per month.
These costs may vary from month to month depending on the required production volume as well as your suppliers. Therefore, keep in mind the possibility of fluctuations in the availability and pricing of supplies.
Cost Accounting
Learn about what cost accounting is and how it works. Includes a free cost sheet template and frequently asked questions.
Sep 27, 2021
4. Direct Labor Budget.
The direct labor budget, similar to the direct materials budget, aims to define how many hours of labor are required to produce each type of product listed in the production budget. This can be somewhat more complex if you decide to break down the hours by each labor category involved.
Determining the total number of labor hours needed to meet the requirements of the production budget helps businesses plan how many employees they will need.
Best Small Business Payroll Software [2024]
Compare different payroll software options, including leading competitors Gusto, TriNet Zenefits, and QuickBooks Payroll. See reviews, pricing info, and FAQs.
May 31, 2024
5. Overhead Budget.
The overhead budget contains all other manufacturing costs. Examples of costs that are assigned to the overhead budget include supervisor salaries, payroll taxes, logistics, rent, and utilities.
On the budget sheet, these costs are typically split into fixed and variable costs. Some items might contain both fixed and variable costs, in which case the differences are noted as such or simply added as a third category of mixed costs.
The cost of the overhead, direct materials, and direct labor together make up what is referred to as the cost of goods sold. Presenting these costs per unit also helps businesses with the development of pricing strategies.
6. Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses.
The costs associated with managing the business and selling and delivering products and services are documented as the selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A).
These are all the direct and indirect expenses of a business that cannot be assigned to a specific product or service the business manufactures or performs. They include items such as management salaries, business licenses, accounting, legal, and human resources expenses, rent, advertising, marketing, and more.
ERP Software
Get pricing and average customer ratings for top ERP Software Platforms. Includes info on ERP for small businesses and answers to FAQs.
Dec 21, 2023
7. Unexpected Expenses.
To avoid being caught off guard by unexpected expenses, it is wise to pad your operating budget a little, leaving room for unforeseen costs. Using your previous years' planned and actual budgets as a reference might give you an idea of how much to put aside. You might decide to determine a specific annual dollar amount or to add a percentage margin to the monthly budgets.
8. Budget Summary and Review.
Once all the sub-budgets have been drawn up, you can move on to creating a budget summary and calculate your anticipated net income. This is done by subtracting all budgeted costs and expenses from the projected revenue.
Net income = Revenue - Costs - Expenses - Unexpected Expenses
The budget can now be reviewed. Determine whether the budget is realistic. You may have to make adjustments. Before changing the numbers in the budget, you will have to consider how you can optimize your operations, perhaps revisit supplier contracts or product lines, and reduce costs and expenses. Since SG&A expenses are not directly linked to production volume, this is usually the first area businesses reassess to cut costs.
10. Budget Tracking.
Keep track of your actual revenue, costs, and income and compare these to your budget on a regular basis. If your actual numbers deviate from your budgeted amounts you will have to investigate what is causing the deviations and may need to adjust your budget or optimize your operations to ensure that your business remains profitable.
FAQs:
What is included in the operating budget?
What is the difference between an operating budget and a capital budget?
A capital budget is used to evaluate potential investments and projects to determine whether they are worth pursuing while an operating budget is used to plan the business's costs and expenses in contrast to its anticipated revenue within a given budget period.
Does an operating budget include salaries?
Yes, salaries are included in an operating budget. Salaries of employees involved in the manufacturing process are listed as direct labor or, in the case of supervisor salaries, as overhead costs. Salaries of general management and other employees not involved in the manufacturing process are usually assigned to the general and administrative expenses in an operating budget.
What are the budget components?
Budget components are the different sub-budgets or budget categories that make up the master budget, including:
What is a budget overview?
A budget overview or summary provides the total budgeted amounts per operational category and the computed net income or profit.
What are operating expenses?
Operating expenses are all the costs associated with running the day-to-day business, such as rent, salaries, sales commissions, marketing, payroll, etc.
Is marketing an operating expense?
Yes, marketing is an operating expense.
What is a line item in a budget?
Line items refer to costs and expenses that are listed by department or cost center in a budget sheet.
Why is an operating budget important?
An operating budget is important for evaluating whether a business has a sufficient net income and allows businesses to plan and optimize their operations to achieve maximum profitability.
What is a cash flow budget?
A cash flow budget is essentially an estimate of the cash inflows and outflows a business anticipates within a given time period, usually on a month-to-month basis.
What is the purpose of an operating budget?
The purpose of an operating budget is to help businesses plan their daily operations and overall profitability. An operating budget is used to estimate the expenses of maintaining daily business operations and expected revenue generated by the operations within a given budget period.
How do I create an operating budget?
- Start by creating a sales budget.
- Prepare a production budget to determine your monthly production requirements.
- Calculate the cost of labor hours and cost of raw materials needed to manufacture the monthly number of products determined in the production budget.
- List and compute all other direct and indirect costs involved in manufacturing your products.
- Determine and compute expenses related to maintaining daily operations that are not linked to the manufacturing process.
- Allow for unexpected expenses by determining a specific dollar amount or a percentage of monthly costs and expenses.
- Take the total amounts computed from each budget above and create a budget summary. Use the final numbers to calculate your net monthly income.
- Review and evaluate your final budget. Make adjustments if necessary.